NMR Lipoprofile Test: How to Read & Interpret Your Results
At the end of your Cardiometabolic Assessment Report, Precision Health Reports also includes a copy of your LabCorp test results every time you have your blood drawn for one of our risk assessments. Although this report has a lot of potentially confusing numbers and letter, we are here to help you understand what it means.
🧩 The NMR Lipoprofile is only one piece of the puzzle to understanding “What is Cardiometabolic Disease?”
📊 Get Your Own Assessment That Includes Your NMR-Measured Lab Results
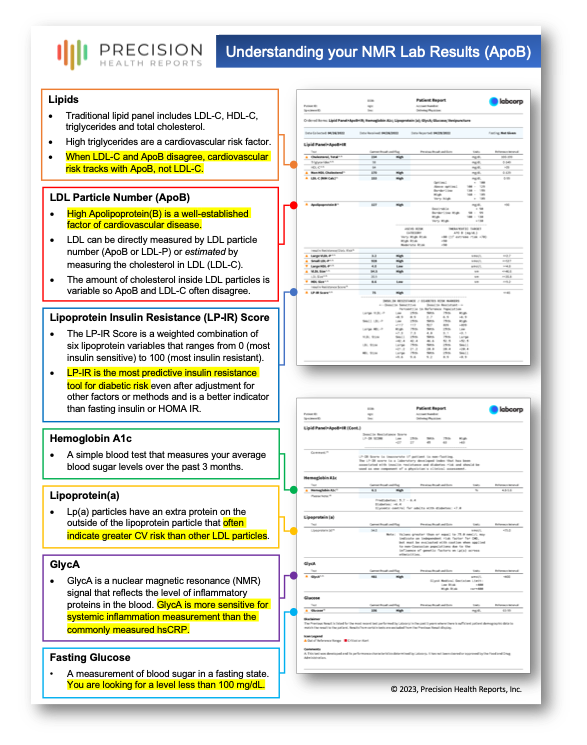
Lipids
Traditional lipid panel includes LDL-C, HDL-C, triglycerides and total cholesterol.
High triglycerides are a cardiovascular risk factor.
When LDL-C and ApoB (or LDL-P) disagree, cardiovascular risk tracks with ApoB (or LDL-P), not LDL-C.
LDL Particle Number (ApoB or LDL-P)
High Apolipoprotein(B) is a well-established factor of cardiovascular disease.
LDL can be directly measured by LDL particle number (ApoB or LDL-P) or estimated by measuring the cholesterol in LDL (LDL-C).
The amount of cholesterol inside LDL particles is variable so ApoB and LDL-C often disagree.
📚 Learn more about the differences between ApoB and LDL-P for atherogenic particle number measurement
LDL and HDL Particles
HDL-P is the direct measure of High Density Lipoprotein (HDL) particles; it has been shown to be more strongly and independently related to cardiovascular risk than HDL Cholesterol (HDL-C).
Small LDL size and increased Small LDL-P are commonly present in individuals with prediabetes, diabetes, and insulin resistance.
Small LDL-P and LDL Size
While Small LDL-P and Small LDL Particle Size are associated with cardiovascular risk, they are not predictive of risk once LDL-P is taken into account.
It is LDL-P, not Small LDL-P or LDL particle size, that is most important in managing cardiovascular risk.
Lipoprotein Insulin Resistance (LP-IR) Score
Lipoprotein changes are one of the earliest manifestations of insulin resistance.
The LP-IR Score is a weighted combination of six NMR lipoprotein variables that ranges from 0 (most insulin sensitive) to 100 (most insulin resistant).
Multiple landmark clinical studies show the higher the LP-IR Score, the greater the risk of developing diabetes.
LP-IR remains predictive of diabetic risk even after adjustment for other factors including age, gender, race, waist circumference, body mass index, family history of diabetes, physical activity, glucose, insulin levels and lipids.
📚 Learn why LP-IR score is the most predictive measurement for insulin resistance.
Hemoglobin A1c
A simple blood test that measures your average blood sugar levels over the past 3 months.
Lipoprotein(a)
Lp(a) particles have an extra protein on the outside of the lipoprotein particle that often indicate greater CV risk than other LDL particles. Learn more about high Lp(a).
GlycA
GlycA is a nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) signal that reflects the level of inflammatory proteins in the blood. GlycA is more sensitive for systemic inflammation measurement than the commonly measured hsCRP.
Fasting Glucose
A measurement of blood sugar in a fasting state. You are looking for a level less than 100 mg/dL.
Are you interested in getting your own NMR Lipoprofile results as part of your own Cardiometabolic Risk Assessment or Advanced Metabolic Health Assessment?
Cardiometabolic Risk Assessment
The most comprehensive risk assessment report in the market is now available directly to you. This report is designed to give you a comprehensive and actionable view of YOUR cardiometabolic health answering the question “what is MY risk for diabetes, heart attack, or stroke and what can I do to reduce MY risk?”
Our Cardiometabolic Risk Assessment gives you a complete picture of your:
Individual metabolic risk factors & Metabolic Syndrome Severity Score.
10-year & Lifetime Cardiovascular Event Risk, risk enhancing factors, and lipoprotein goals.
8-year Diabetic Risk and Lipoprotein Insulin Resistance Score (LP-IR).
Labs included: NMR-measured ApoB or LDL-P and cholesterol, insulin resistance, lipoprotein (a), hemoglobin A1C, glucose, and GlycA inflammation biomarkers.
Do you want to know more? Take a deeper dive into the details of our complete Cardiometabolic Risk Assessment, learn more here.
The Advanced Metabolic Health Assessment is a slimmed-down version of the Cardiometabolic Risk Assessment. It is focused on metabolic health and diabetic risk only, while leaving out the cardiovascular risk portion that is sometimes distracting to people who are working on metabolic health first/only.
Our Advanced Metabolic Health Assessment gives you a complete picture of your:
Individual metabolic risk factors & Metabolic Syndrome Severity Score.
8-year Diabetic Risk and Lipoprotein Insulin Resistance Score (LP-IR).
Labs included: NMR-measured ApoB and cholesterol, insulin resistance, hemoglobin A1C, and fasting glucose.
Do you want to know more? Take a deeper dive into the details of our complete Advanced Metabolic Health Assessment, learn more here.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions about the NMR Lipoprofile
What is an NMR Lipoprofile test?
The NMR Lipoprofile is an advanced blood test that uses nuclear magnetic resonance technology to measure the number and size of lipoprotein particles in your blood. Unlike a standard cholesterol test, it provides a more detailed picture of your cardiovascular risk.
How is an NMR Lipoprofile different from a standard cholesterol test?
A standard lipid panel reports cholesterol content (LDL-C, HDL-C, total cholesterol, triglycerides). The NMR Lipoprofile measures LDL particle number (LDL-P), which reflects how many LDL particles are present, regardless of how much cholesterol each particle carries. More particles mean more chances for them to enter the artery wall and contribute to plaque.
What is LDL-P and why does it matter?
LDL-P stands for LDL particle number. Research shows that LDL-P is often a better predictor of heart attack and stroke risk than LDL cholesterol levels alone, especially when LDL-C and LDL-P results don’t match (called “discordance”).
How do you interpret NMR Lipoprofile results?
Interpretation usually focuses on LDL-P. A higher LDL-P suggests higher cardiovascular risk. Your provider may also look at particle size, HDL particle number, and triglyceride-rich lipoproteins for a more complete view of metabolic health. Always interpret results in the context of your overall cardiometabolic risk.
Who should consider an NMR Lipoprofile?
The test can be especially helpful for people with a family history of heart disease, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, borderline cholesterol results, or unexplained cardiovascular risk. It can provide clarity when standard cholesterol testing leaves uncertainty.
How does Precision Health Reports use the NMR Lipoprofile?
Within our Cardiometabolic Risk Assessment, the NMR Lipoprofile provides particle-based insights that are combined with other proven biomarkers (such as ApoB, LP-IR score, GlycA, and Lp(a)) and clinical history. This allows for the most accurate, personalized assessment of risk and an actionable prevention plan.
📚 Learn More About the NMR Lipoprofile and LDL-P
American College of Cardiology. Discordance Between LDL Cholesterol and LDL Particle Number in Predicting Cardiovascular Risk. ACC.org
National Lipid Association. NMR Lipoprotein Testing and Cardiovascular Risk Assessment. lipid.org
Mora S, Otvos JD, Rosenson RS, et al. LDL Particle Subclass Measurements by NMR and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease. Journal of Clinical Lipidology. 2015.
Cromwell WC, Otvos JD. Low-Density Lipoprotein Particle Number and Risk for Cardiovascular Disease. Current Atherosclerosis Reports. 2004.
Sniderman AD, et al. Apolipoprotein B and Particle Number as Predictors of Cardiovascular Risk. Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC).